Featured Posts on Lesson Plan
Mathematics Lab Activity-2 Class XI
- Get link
- X
- Other Apps
Mathematics Lab Activity-2 Class XI
Chapter - 1 | Set Theory
Activity - 2
Objective
To represent set theoretic operations using venn diagrams.
Material Required
Hardboard, white thick sheets of papers, pencils, colors, scissors, adhesive.
Theory
Venn Diagrams
Most of the relationships between the sets can be represented by diagrams, which are known as venn diagrams. In these diagrams the universal (U) set is represented by a rectangle and all other subsets are represented by circles.
Operations on sets
1. Union of sets : The union of two sets A and B is the set C which consists of all the elements of A and B, the common elements being taken only once
A ⋃ B = {x : x ∈ A or x ∈ B}
2. Intersection of sets : The intersection of two sets A and B is the set of all elements which are common to both A and B
A ⋂ B = {x : x ∈ A and x ∈ B}
3. Difference of set : Difference of set A and B is the set of all elements which belongs to A but not to B.
A – B = {x : x ∈ A and x ∉ B}
4. Complement of a set : If ⋃ is a universal set and A is a subset of ⋃ , then complement of set A is the set of all elements of ⋃ which are not the elements of A. Complement of set A is denoted by A'
A' = {x : x ∈ ⋃and x ∉ A} ⇒ A' = ⋃ - A
Complement of the complement is the set itself or (A')' = A
Procedure
1. Cut rectangular strips from the sheet of paper and paste them on a hardboard. Write the symbol U in the left or right top corner of the rectangle. U denotes the universal set represented by the rectangle.
2. Draw circles inside each of the rectangular strips and shade different portions as shown in the following figures.
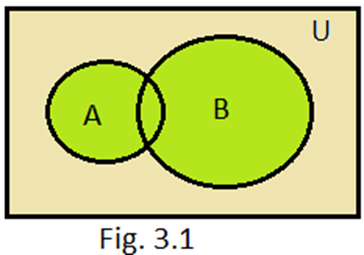
3. Coloured portion in figure 3.1 represent A ⋃ B.
4. Coloured portion in figure 3.2 represent A ⋂ B.
5. Coloured portion in figure 3.3 represent (A')
6. Coloured portion in figure 3.4 represent (B').
7. Coloured portion in figure 3.5 represent (A⋂B)'
8. Coloured portion in figure 3.6 represent (A⋃B)' .
9. Coloured portion in figure 3.7 represent A' ⋂B = B – A
10. Coloured portion in figure 3.8 represent A'⋃B
11. Figure 3.9 represent A⋂B = ф
12. Figure 3.10 represent A⊂B
Observations
1. Coloured portion in figure 3.1 represent A ⋃ B.
2. Coloured portion in figure 3.2 represent A ⋂ B.
3. Coloured portion in figure 3.3 represent (A').
4. Coloured portion in figure 3.4 represent (B').
5. Coloured portion in figure 3.5 represent (A⋂B)'.
6. Coloured portion in figure 3.6 represent (A⋃B)' .
7. Coloured portion in figure 3.7 represent A' ⋂B = B – A
8. Coloured portion in figure 3.8 represent A'⋃B
9. Figure 3.9 represent A⋂B = ф
10. Figure 3.10 represent A ⊂ B
Result
Theoretical operations can be represented using venn diagrams. Venn diagrams become easy to understand.
Applications
Set theoretic representations of venn diagrams are used in Logic and Mathematics.
VIVA – VOICE
Q. 1. What are venn diagrams?
Ans. The diagrams used to represent relationships between sets are called Venn diagrams.
Q. 2. How are Venn diagrams represented?
Ans. Venn diagrams are represented by rectangles and closed curves, usually circles.
Q. 3. How is the universal set represented?
Ans. The universal set is represented by rectangle.
Q. 4. How are the subsets of the universal set represented?
Ans. Subsets of universal sets are represented by circles.
Q. 5. How are the elements of the sets are written in venn diagrams?
Ans. In venn diagrams, the elements are written in their respective circles.
Q. 6 What is A⋃ ф equal to ?
Ans. A⋃ ф = A, where ф is an empty set.
Q. 7 What are disjoint set ?
Ans. Two sets A and B are said to be disjoint sets if , A⋂B = ф , where ф is the empty set.
Q. 8 Define complement of a set.
Ans. The complement of a subset A of the universal set U is the set of all element of U, which are not the elements of A.
THANKS FOR YOUR VISIT
PLEASE COMMENT BELOW
- Get link
- X
- Other Apps














Comments
Post a Comment