Featured Posts on Lesson Plan
Lesson Plan, Class XI (Ch-2) | Relations & Functions
- Get link
- X
- Other Apps
LESSON PLAN MATHEMATICS CLASS 10+1
- Ordered pair, Cartesian product of sets. Number of elements in the Cartesian product of two sets.
- Cartesian product of the sets of reals with itself (up to R x R x R )
- Definition of relation, pictorial diagrams, domain, co-domain and range of a relation.
- Function as a special type of relation, pictorial representation of a function, domain, co-domain and range of a function.
- Real valued functions, their domain and range.
- Constant, identity, polynomial, rational, modulus, signum, exponential, logarithmic and greatest integer functions with their graphs.
- Sum, difference, product and quotient of functions.
- Cartesian product of two sets.
- Numbers of subsets and number of relations from cartesian product.
- Domain, Range and Codomain of relations.
- Definition of function and types of functions.
- Domain and range of different types of functions.
- Operations on functions.
NCERT Text book of Mathematics
NCERT Exemplar Text Book
RESOURCE CENTRE at cbsemathematics.com
DAV Resource Material for class 10
Relations, Functions, Domain, Range, Codomain, Cartesian Product, Modulus functions, Logarithmic functions, Signum functions, Greatest Integer functions
- Cartesian Product of two sets.
- Number of relations from cartesian product.
- Domain, range and codomain of relations.
- Definition of functions.
- Domain and range of functions.
- Different types of functions.
INTRODUCTORY ACTIVITY : Click Here
In the above figure
A X B = {(a1, b1), (a1, b2), (a1, b3), (a2, b1), (a2, b2), (a2, b3) }
n(A) = 2, n(B) = 3, n(A X B) = 2 x 3 = 6
Number of subsets of A x B = 26 = 64
Number of relations of A X B = 26 = 64
Function their Domain, Range & Co-domain
FunctionSome Functions And Their Graphs
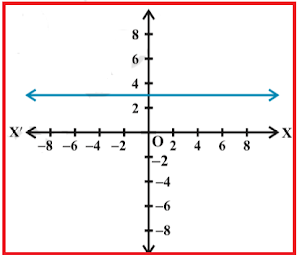
Constant Function :
For the constant function f(x) = c, the domain consists of all real numbers; there is no restrictions on the input. The only output value is the constant c, so the range is the set {c} that contains this single element. In interval notation, this is written as [c, c].
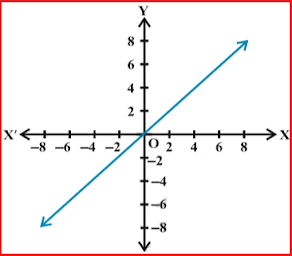
Identity Function :
For the identity function f(x) = x, there is no restriction on x. Both domain and range are the set of all real numbers.
Modulus Function :
For the absolute value function f(x)=|x|, there is no restriction on x (domain). However, because absolute value is defined as a distance from 0, the output (range) can only be greater than or equal to 0.
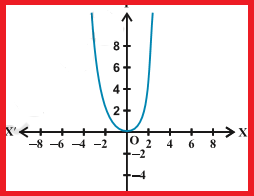
Quadratic polynomial Function :
For the quadratic function f(x) = x2, the domain is all real numbers because the horizontal extent of the graph is the whole real number line. Since the graph does not include any negative values for the range, the range is only non-negative real numbers.
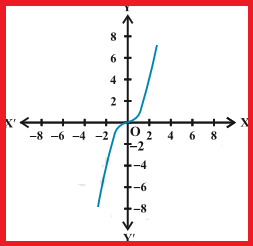
Cubic Polynomial Function :
Reciprocal Function
For the reciprocal function f(x)= , we cannot divide any number by 0, so we must exclude 0 from the domain. Further, 1 divided by any value can never be 0, so the range also will not include 0.
Reciprocal Squared Function
For the reciprocal squared function f(x) = , we cannot divide by 0, so we must exclude 0 from the domain. There is also no x that can give an output of 0, so 0 is also excluded from the range as well. Note that the output (Range) of this function is always positive due to the square in the denominator, so the range includes only positive Real numbers.
Square Root Function:
For the square root function f(x)= , we cannot take the square root of a negative real number, so the domain must be 0 or greater than "0". The range also excludes negative numbers because the square root of a positive number x is defined to be positive square root of negative number is negative.
Cube Root Functions
For the cube root of a function f(x) = , the domain and range include all real numbers. Note that cube root of positive number is positive and cube root of negative number is negative.
Signum Function :
Greatest Integer Function
Undefined Terms :
- Review questions given by the teacher.
- Students can make a pictorial representation showing relation and functions with their domain, co-domain and range.
- Solve NCERT problems with examples and some extra questions from refreshers.
- Get link
- X
- Other Apps
Comments













This comment has been removed by the author.
ReplyDelete